Headings help everyone to better understand your content by establishing information grouping and prioritization. Headings should be properly identified as such and should be used in chronological, nested order.
 What does this mean?
What does this mean?
Headings are not just denoted visually by changing the font size or making text bold. Headings are specific text styles built-in to Microsoft Word, website editors, and PDFs. These styles are essential for assistive technology to identify text as a heading.
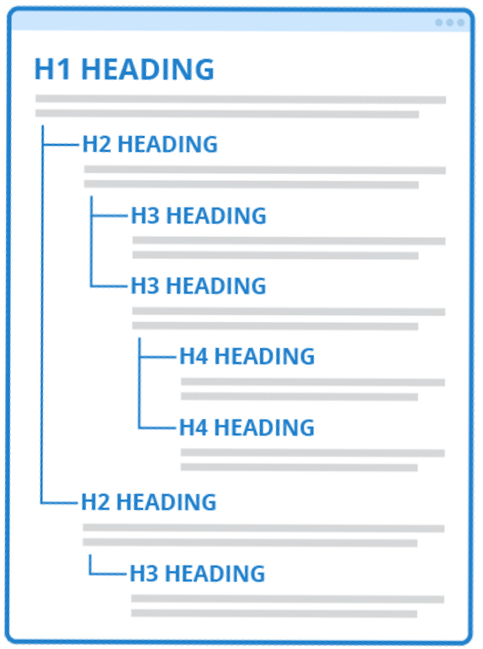
Headings are usually referred to by their heading level. Heading levels denote the structure of information by informing users about the level of importance and if the information falls under a previous heading as well. Headings are denoted numerically beginning with Heading level 1 or simply Heading 1 (H1). There can be as many subsequent heading levels as is necessary but it is rare for the structure of digital content to necessitate levels beyond Heading level 5.
- Heading level 1 is most commonly used as a title of your webpage or document.
- Then, any main headings after this title would be Heading level 2.
- If there is information nested within a Heading level 2 that needs more organization and structure, you would use a Heading level 3.
- If this was the case under a Heading level 3, you would use Heading level 4 and so on.
- If there is information nested within a Heading level 2 that needs more organization and structure, you would use a Heading level 3.
- Then, any main headings after this title would be Heading level 2.
Application
Use a single Heading 1 for your document or webpage and set it as a descriptive title for the content. Please note that Drupal webpages automatically set the Title as a Heading 1. Be sure to give every webpage a title in the designated text box.
Follow the proper nesting of heading levels described above and do not skip any heading levels (i.e. do not use a Heading 2 followed by a Heading 4). Follow the directions below for your specific format to properly set text as a heading. If you need assistance with implementing headings in other formats, please reach out to accessibility@pitt.edu.
Microsoft Word
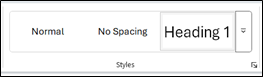
- Select the Home tab in the top ribbon.
- In your document, select the text to convert to a heading.
- Click on the appropriate heading level in the “Styles” gallery.
Drupal
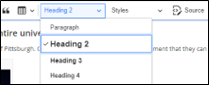
- In your webpage editor, select the text to convert to a heading.
- Select the Headings drop down from the toolbar.
- Click on the appropriate heading level.
Please note that you do not have to keep the visual appearance the same as is default for any headings. In Word, visual changes can quickly be implemented across all headings by right-clicking on the Heading level in the “Styles” gallery and selecting “Modify” or “Update Heading to Match Selection.” In Drupal, visual changes must be implemented individually.
Impact
Headings establish clear structure that benefits both disable and non-disabled users. Those using assistive technology rely on headings to be able to quickly move through content and understand the outline of information without visual aid. Without using built-in styles for headings, there is no way for a blind user to understand that a heading’s text is more important than any of the rest of the text. Using headings in the proper chronological and nested order helps avoid confusion for these users as well such that they do not think that they have missed any content.
The proper use of headings also helps visually break up content so that it is easier for sighted users to read. Large blocks of text with no breaks or headings can be time-consuming and eye-straining to read in a digital space. Headings help all users to find the information they need quickly without frustration or pain.
